Moderate Sedation Vital Sign Monitoring
The most important monitor used during IV moderate sedation is that for the central nervous system CNS through direct verbal contact with and the response of the patient. ECG monitoring should be continuous.
Sedation Monitoring And Post Sedation Recovery And Discharge
The registered nurse is responsible for monitoring the patients status medications and vital signs.

Moderate sedation vital sign monitoring. True False 10 minutes 6. I vital signs to include blood pressure pulse respiratory rate and oximetry results. Exceptions to this requirement and the reason for such exceptions must be documented.
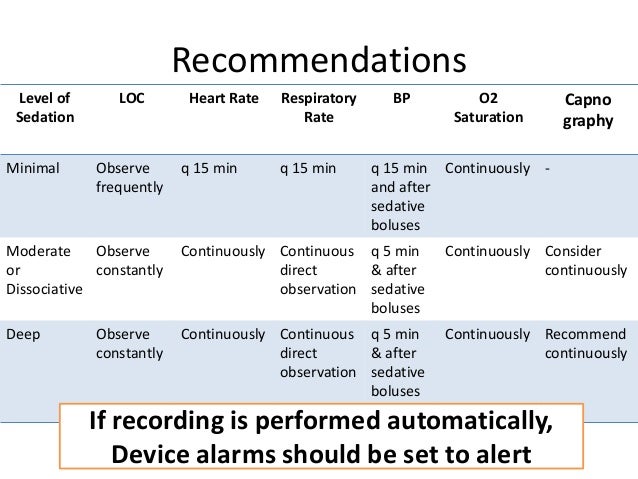
Regular monitoring of these vital signs eg every 15 minutes q 15 min or every 5 minutes q 5 min is suggested. During basic procedural sedation patients vital signs including level of consciousness should be documented every 15 minutes. IV Sedation Procedure - Monitoring the Sedated Patient The most important body functions that are monitored during an IV Sedation procedure are breathing pulse blood pressure and oxygen saturation.
Monitor vital signs before during and after the procedure. First IV access must be maintained. Consider monitoring exhaled carbon dioxide through capnography for patients whose ventilation cannot be directly.
Weight and height BMI. A The use of moderate sedation must be documented in the patients medical record. By definition of moderate sedation patients should be able to respond appropriately to verbal or physical stimulation throughout parenteral moderate sedation procedures.
All patients scheduled to receive conscious sedation must be assigned an ASA grade. Consciousness is another important monitoring parameter. Although cognitive function and coordination may be impaired ventilation and cardiovascular functions are unaffected.
Cardiac rhythm monitoring is required for the following. Monitoring of the heart rate and rhythm at regular intervals is desirable during parenteral sedation techniques such as intramuscular IM intranasal IN and intravenous IV sedation. Third patients should be protected from pressure-related and position-related injuries.
Patients undergoing moderate sedation should maintain the ability to respond to simple verbal or tactile stimulation. The other moderate sedation codes 99151 99152 99155 99156 and 99157 are assigned a 9 indicating the TCPC concept doesnt apply. B Appropriate monitoring of vital signs must be done throughout the procedure for which moderate sedation is being administered and documented at 5-minute intervals.
Remember the patient has to protect their own airway they breathe on their own but they have an altered perception of pain and some amnesia. The ACR-SIR guidelines provide specific recommendations for the in-procedure monitoring and management during moderate sedation. Moderate to Deep Sedation If the patient goes from Moderate Sedation to Deep Sedation the person monitoring the patient.
Makes the MD doing the procedure aware Helps patient maintain open airway oral airway head tilt-chin lift jaw thrust Assists with ventilations via Ambu Bag. 2 The minimum standards for monitoring moderate sedation patients shall include the following. Second homeothermia should be preserved.
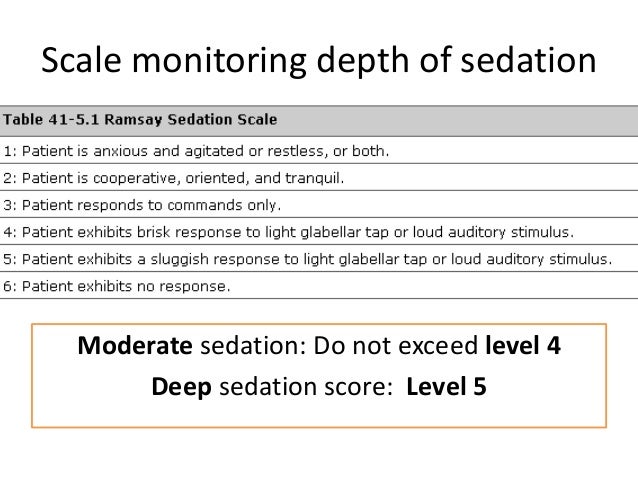
Patients who have a history of cardiac disease. This is for identification of the level of sedation intended for the patient the actual patient response to the sedation medications and recognition when the level of sedation is deeper than intended and how to rescue the patient. Moderate sedation is a drug induced state we place patients in so that they can withstand a procedure comfortably.
These can be checked by a combination of clinical monitoring and use of electronic equipment. Moderate Sedation Protective reflexes are intact Airway remains patent Spontaneous ventilation is adequate Patient responds to physical stimulation or verbal command No adverse effect on. Minimal sedation or anxiolysis a drug induced state during which patients respond normally to verbal commands.
Patients who are ASA Class III IV or V. Specific time frames are discussed later in this chapter but a basic rule of thumb is that. The NA is not in the FACILITY NA INDICATOR column for these other codes.
There are different RVU values for facility and non-facility site of service. Moderate Monitoring Requirements - the following should be monitored. Once moderate sedationanalgesia is established continually monitor blood pressure eg at 5-min intervals and heart rate during the procedure unless such monitoring interferes with the procedure eg magnetic resonance imaging where stimulation from the blood pressure cuff could arouse an appropriately sedated patient.
In order to compare and contrast the levels of sedation it. Patients who have been given benzodiazepines should be instructed to avoid operating a car consuming alcohol or signing legal papers for 24 hours after receiving the medication. In some facilities and states the RN administers moderate sedation check your state board of nursing.
Fourth all patients should be continuously monitored throughout the procedure by.

Moderate Conscious Sedation Coding Guidelines Sedation Medical Billing And Coding Coding
Sedation Monitoring And Post Sedation Recovery And Discharge

Monitoring Requirements For Different Anesthetic And Sedation Techniques Download Table
